By Athanasios Pitatzis
This article was first published in the Summer Edition of International Petroleum Student Magazine YoungPetro, http://issuu.com/youngpetroart/docs/nr-18-summer-6.07.16-internet-stron/1?e=6136758/37462422 (Pages 17-23)
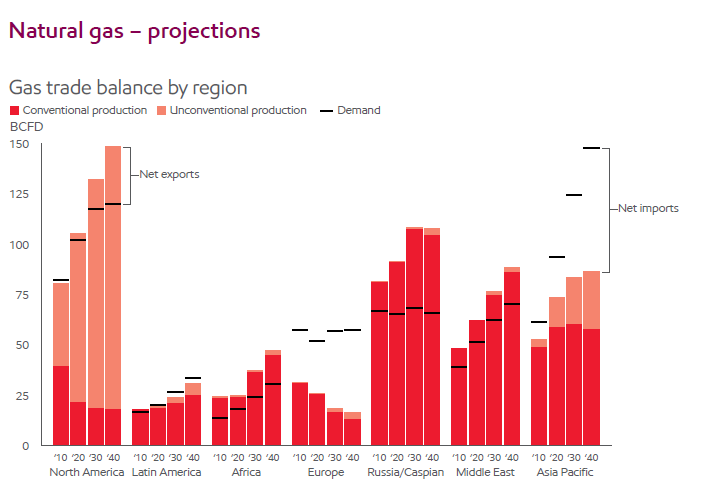
According to Exxon Mobil Outlook for Energy 2016 report, global demand for natural gas is seen rising by 50 percent from 2014 to 2040, faster than most other fuels and more than twice as fast as oil. In the same report, Exxon Mobil claims that nearly half the growth in global gas demand through 2040 is expected to be met through inter-regional trade, most of it using LNG. Also, Exxon Mobil predicts that by 2040, Asia Pacific is projected to get more than 40 percent of its gas from other regions, and likely will have overtaken Europe as the world’s largest net gas importer.
Natural Gas Projections, Source: The Outlook for Energy 2016 Version | ExxonMobil. Retrieved May 13, 2016, from http://corporate.exxonmobil.com/en/energy/energy-outlook
According to U.S Energy Information Administration (EIA, International Energy Outlook 2016 report), one other hopeful prediction for global natural gas demand is that consumption of natural gas worldwide is projected to increase from 120 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) in 2012 to 203 Tcf in 2040. Furthermore, EIA in the same report predicts that World LNG trade will increase significantly, from about 12 Tcf in 2012 to 29 Tcf in 2040. As far as South – East Asia (OECD Asia and NON-OECD Asia countries) gas future demand EIA in the International Energy Outlook 2016 report predicts that will increase from 22,4 Tcf in 2012 to 63 Tcf in 2040.
South – East Asia LNG market has two categories, the first one is the mature LNG markets and the second one is recent and emerging Asia LNG Markets. Asia LNG mature markets include:
- Japan
- South Korea and
- Taiwan
On the other hand, recent and emerging Asia LNG markets include:
- China
- India
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Pakistan
- Bangladesh
- Vietnam
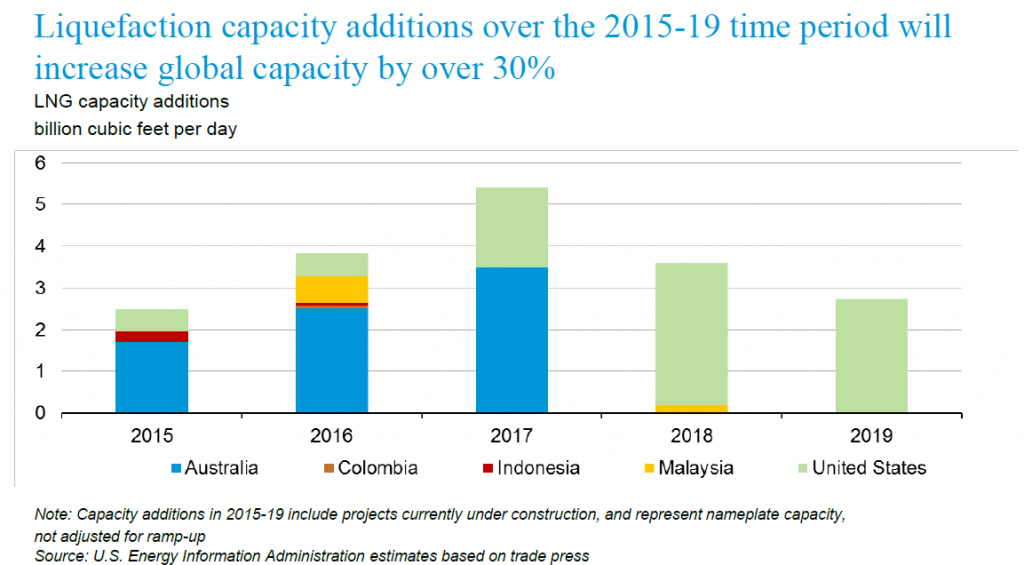
According to EIA until 2019 Global Liquefaction capacity will increase by 30 percent.
Future Liquefication capacity until 2019, Source: International Energy Outlook 2016-World energy demand and economic outlook – U.S Energy Information Administration. Retrieved May 12, 2016, from http://www.eia.gov/forecasts/ieo/world.cfm
China LNG Future Imports
China LNG future imports will be an essential element for the global LNG suppliers (current and future players) survival. Recent statements from the International Energy Agency (IEA, 2015 World Energy Outlook report) predicts that China future gas demand will be 315 bcm/y for 2020. China future gas demand will determine from these factors:
- The future Chinese energy mix with an increasing role of nuclear and renewables and a decreasing role of coal
- Future China Economic growth
- China next economic model will move or not to a lower carbon-intensive economy
- China future natural gas reforms regarding their domestic gas market, for example, the liberalization of China natural gas market
- Political Instability
- Fast growing aging population
It is evident from the above inputs that future China natural gas demand faces many uncertainties, and accurate predictions cannot be made.
China Historical and Future Natural Gas Demand from Various Sources, Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
One other key element which will determine the future Chinese LNG imports is the future China natural gas production. A major percentage of this future gas production is estimated to produce from the China vast shale gas reserves. Despite the potential and the momentum the development of China shale/conventional gas reserves face many challenges. These key challenges as I have mentioned already in one of my previous articles are:
- Uncertainty in water supply, which is necessary for the development of shale gas reserves during the process of fracking
- Monopoly over pipelines network
- Monopoly over exploration rights
- Unfair competition between China NOCs and International Oil Companies (IOCs)
- Imperfect policy system
- Poor infrastructure
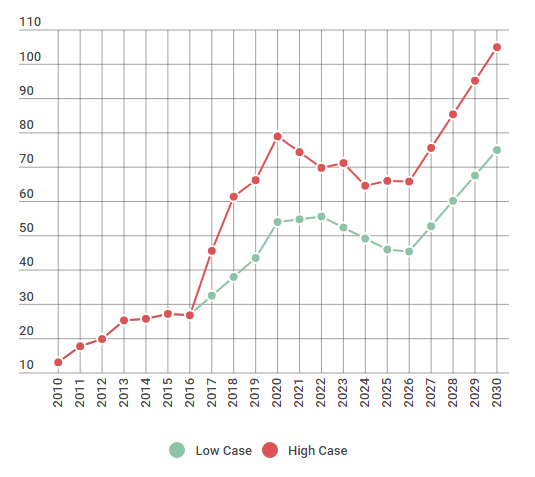
In conclusion, according to Howard V Rogers and its report “Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook” on Oxford Institute for Energy Studies the future China LNG imports has two possibly scenarios. (Observe the graphs below)
China Future LNG Imports – Low and High Cases (Bcm/y), Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
The main gas pipelines routes from which China import gas are:
- Pipeline Imports – Myanmar
- Pipeline Imports – Turkmenistan & Central Asia
- Pipeline Imports – East Siberia
- Pipeline Imports – West Siberia
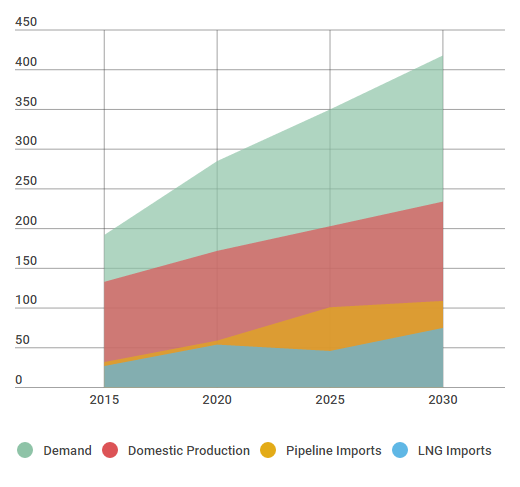
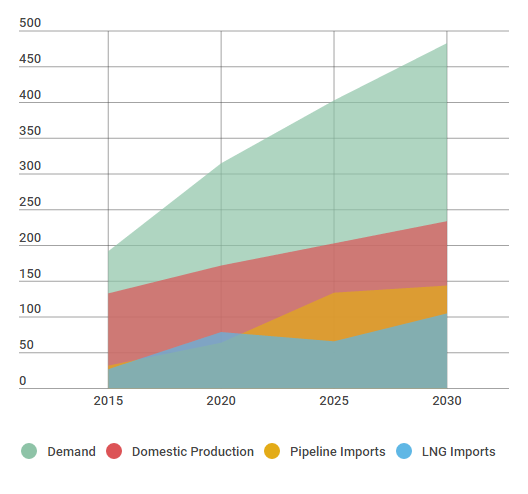
China Supply and Demand on Base-Low Case Demand Assumptions bcm/y, Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
China Supply and Demand on High Case Demand Assumptions bcm/y, Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
Japan Future LNG Imports
The main factors which will determine the Japan future LNG imports are:
- The different scenarios for nuclear factories re-starts for power generation
- The proportion of the renewables in the future energy mix
- If the country achieves the energy efficiency targets which have already set
- If Japan can achieve or not in the future an economical extraction of its vast Methane Hydrates deposits
- Future Stable Economic Growth
- Future Energy Reforms in electricity and natural gas market
- Unpredicted natural disasters like earthquakes or tsunamis which can affect the energy policy of Japan
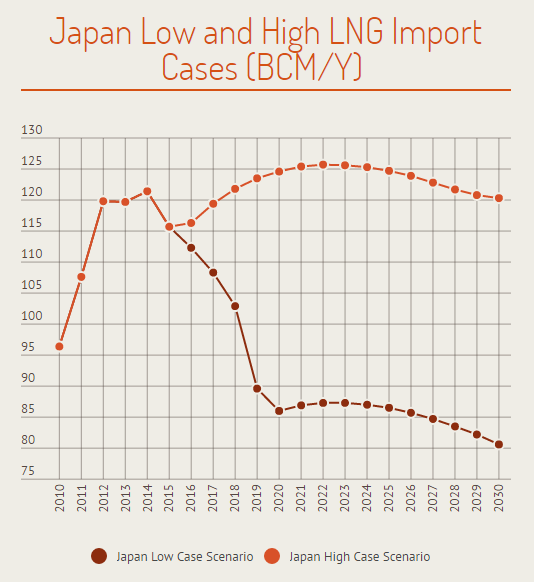
Japan Future LNG Imports – Low and High Cases (Bcm/y), Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
India Future LNG Imports
Some of the key threats – challenges for the future India LNG imports are:
- The increasing role of the coal in the India energy mix
- India economy current and future growth is weak due to many factors such as corruption, poor infrastructure, and fiscal deficits
- India future domestic shale/conventional gas production
- Political Instability
- Geopolitical Tensions with Pakistan
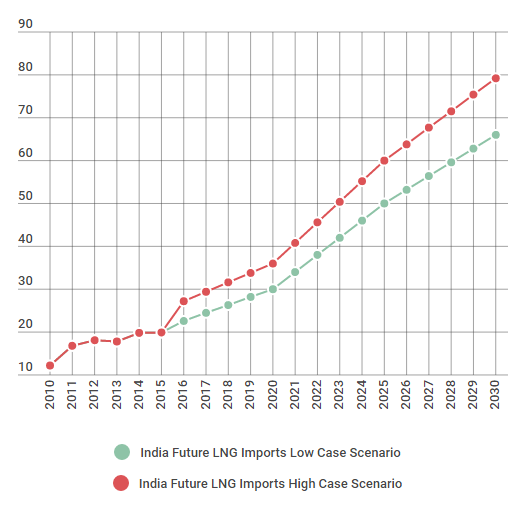
India Future LNG Imports – Low and High Cases (Bcm/y), Source: Asian LNG Demand: Key Drivers and Outlook Report, Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, Retrieved 12 June of 2016, https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/asian-lng-demand-key-drivers-outlook/
Asia LNG Future Demand and Supply Balance
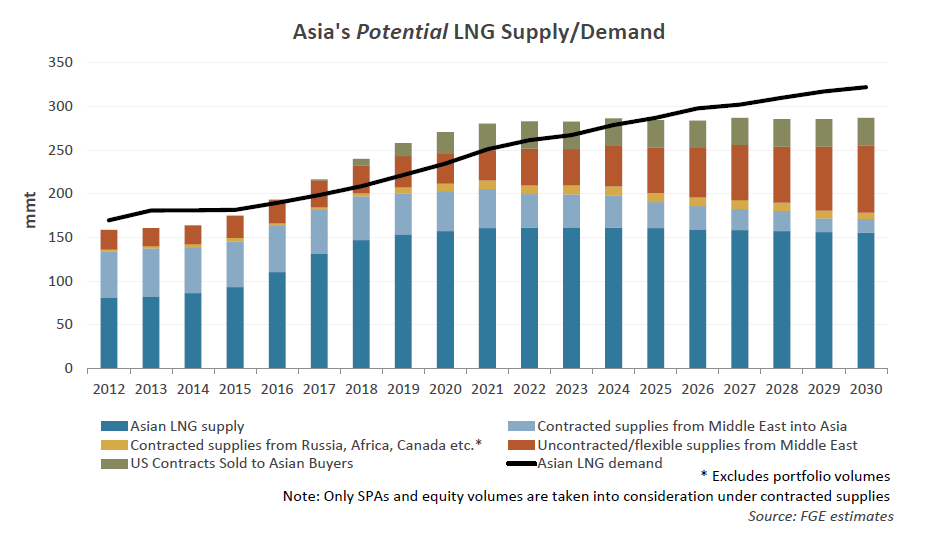
Asia’s Potential LNG Supply/Demand, Source: Global LNG Hub, Facts Global Energy Company Presentation A New World Oil Order Emerging in 2016 and Beyond?, By Dr. Fereidun Fesharaki, Chairman, February 18, 2016, Australian Institute of Energy, Sydney, Australia, http://www.globallnghub.com/
Based on the above graph it is evident that Asia LNG market is oversupplied and will be for the next 8-9 years, this means that LNG spot prices in Asia will remain flat for a long time. My personal estimation is that we can see Asia LNG spot prices between 4-6$ per MMBtu until 2022 at least. Furthermore, due to the future, an extended period of low LNG prices many projects for LNG exports terminals will not get an FID and exist plants which are under construction in a case of future small Asia LNG imports will face many economic challenges.
Conclusion
The primary outcomes from our analysis for the Global LNG Industry are:
- LNG exporters will have small amount of profits for many years
- National, regional and international policies will affect the future Asia LNG demand significantly
- Technological improvements and decreasing costs of renewables and storage of energy can challenge significantly the future development of the LNG industry worldwide
- Europe can be a new destination for Qatar and the USA LNG exports which were estimated to exported to Asia
- Decreasing both capital and operating costs for the developers of new projects will be a major target
- LNG exporters will participate in cooperation with LNG buyers in future LNG receiving terminals with general business aim to increase the LNG demand worldwide
- Changing in the future contracts of the LNG market
Athanasios Pitatzis is an Industrial/Petroleum Engineer and Member of the Greek Energy Forum. He specializes in the development of oil & gas markets in Southeast Europe and the Mediterranean. Also, he is the owner of the website Energy Routes in which he publishes all of his articles for global oil and gas industry, http://energyroutes.eu/ The opinions expressed in the article are personal and do not reflect the views of the entire forum or the company that employs the author. Follow Greek Energy Forum on Twitter at @GrEnergyForum and Athanasios at @thanospitatzis.



Leave a comment