This article was first published in the Spring Edition of International Petroleum Student Magazine YoungPetro, http://issuu.com/youngpetroart/docs/24.04-youngpetro-spring17-internet-/1?e=6136758/35254700 on Pages 23-27
By Athanasios Pitatzis
The global low LNG prices of the last two years have created a significant challenging business environment for many LNG exports projects. Current and future global LNG demand seems very gloomy. According to the recent KPMG report for global LNG markets with the title “Uncharted waters: LNG demand in a transforming industry” global LNG demand will face many uncertainties in the future. The same report mentions that the factors which will affect the future global LNG demand are:
In short term:
- Japanese nuclear restarts
- Ukraine crisis
- LNG storage
- Trading house vertical integration
In medium term:
- New buyer alliances (JERA)
- Japanese deregulation
- Chinese economic growth
- New Russian pipelines
- New importers
In long term:
- Asian urbanization
- LNG in transport
- Renewable energy
- Climate policy
Exxon Mobil predicts in their report (published for the year 2016) with tittle “The Outlook for Energy: A View to 2040” that:
- Global demand for natural gas will increase by 50 per cent from 2014 to 2040
- Natural gas is projected to cover the 40 per cent of the future global energy demand until 2040
- LNG exports expected to triple globally by 2040
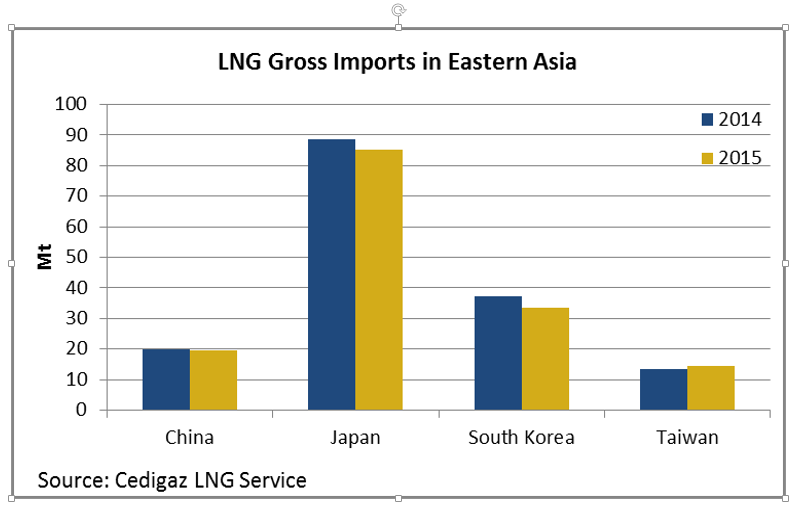
It is obvious that LNG industry has a bright long – term future ahead but the next five years will be challenging. Major LNG importers for the year 2014 according to the International Gas Union were Japan, South Korea, China, India, Taiwan and the UK. The same year the major LNG exporters were Qatar, Malaysia, Australia and Nigeria. Until 2020 many LNG export facilities will come online mainly in the USA and to Australia. East Asia LNG imports have declined by 3.9 percent in 2015 in comparison with 2014. The main factors for this decline according to Cedigaz (the international association for natural gas) were unexpected low economic growth in that region, gas-fuel competitiveness and weather related factors.
LNG Gross Imports in Eastern Asia, Source: Cedigaz, EASTERN ASIAN LNG GROSS IMPORTS DECLINED BY 3.9% IN 2015 TO 152.8 MT, 12/02/2016,http://blog.cedigaz.org/eastern-asian-lng/
Moreover, LNG market is transforming to a global united commodity market with increasing liquidity and competitive market all over the world. These markets conditions will continue until 2020 or 2022. The decline in LNG prices is more than 50 percent in some cases in a period of only three years from 2013 to 2016. (Observe the pictures below)
World LNG prices January 2013, Source: USA Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) https://www.ferc.gov/
World LNG prices January 2016, Source: USA Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) https://www.ferc.gov/
Differences in LNG prices from 2013 to 2016 per destination:
The prices estimated to $US/MMBtu
- Japan: From 15.38$ (January 2013) to 5.75$ (January 2016), a decline of 63%.
- China: From 15.00$ (January 2013) to 5.60$ (January 2016), a decline of 63%.
- UK: From 10.47$ (January 2013) to 4.65$ (January 2016), a reduction of 56%.
- Rio de Janeiro: From 12.10$ (January 2013) to 5.69$ (January 2016), a decrease of 53%.
It is obvious from the above information and LNG market trends that global LNG industry faces many uncertainties.
New emerging LNG markets
According to Energy Insights article with title “New LNG markets to carry future growth in demand” the future emerging LNG importers will be:
- Vietnam
- Uruguay
- South Africa
- Bangladesh
- Bahrain
- El Salvador
- Philippines
- Ghana
- Cuba
- Morocco
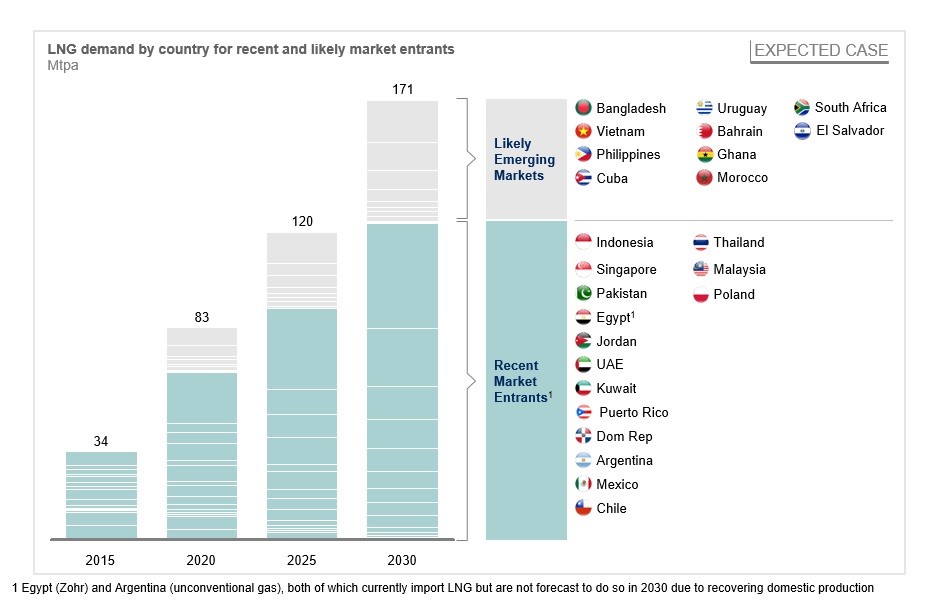
LNG Demand by country for recent and likely market entrants, Source New LNG markets key to growth | Energy Insights. Retrieved March 23, 2016, By James Walke, from https://www.mckinseyenergyinsights.com/insights/new-lng-markets-key-to-growth.aspx
According to the above picture the recent LNG market entrants are Indonesia, Singapore, Pakistan, Egypt (after the Zohr discovery Egypt will be an importer of gas only for the upcoming 2-3 years), Jordan, UAE, Kuwait, Puerto Rico, Dom Rep, Argentina (due to high shale gas reserves the country gas domestic production will recover in the near future), Mexico, Chile, Thailand, Malaysia and Poland. Most of the recent entrants are utilizing floating LNG storage and regasification unit (FSRU). This option to import natural gas from countries which needed is quicker and cheaper than a land-based LNG import terminal.
FSRU Market
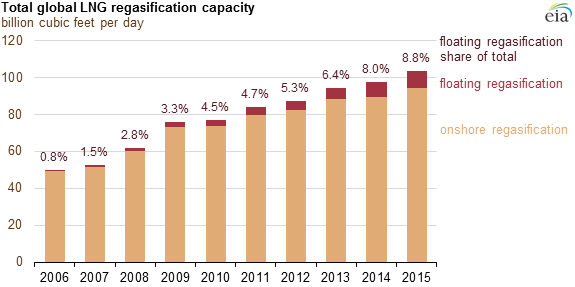
The FSRU market is rising and is a new trend in global LNG market. The first FSRU was first deployed in North America, more particular in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico in 2005.Also, FSRU is a cost-effective solution for smaller or seasonal markets. FSRU are distributed around the world from South America to Europe and the Middle East. Finally, the future outlook for these vessels is promising due to emerging LNG importers like India and Philippines will use this option to import LNG shortly (2016 – 2017).
Total global LNG regasification capacity, Source: Floating LNG Regasification is used to meet rising natural gas demand in smaller markets – Today in Energy – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (n.d.). Retrieved March 23, 2016, from http://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.cfm?id=20972
Future global LNG demand until 2020
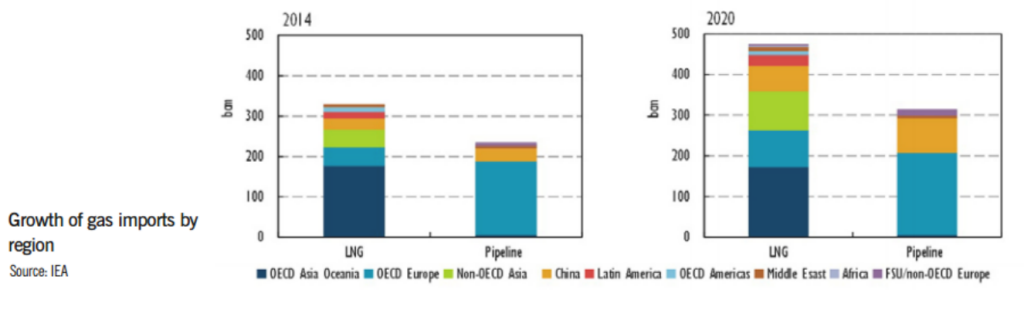
Growth of gas imports by region, Source: International Energy Agency (IEA)
According to the IEA chart, the future LNG demand until 2020 will be generated mainly from Europe, China, India and Middle East.
Conclusion
The LNG glut according to many LNG experts like Cedigaz and IEA is more likely to last until 2022. According to the Gas Strategies during 2016 8 LNG import terminals are planning to start – up with a total capacity of 42.3 mtpa. Most of these terminals located in China (5), one in France, one in Ghana and one in Colombia. At the same time, according to the Gas Strategies 15 LNG exports projects are targeting to get FID (Final Investment decisions) during 2016. Most of these projects located in the US, Canada, and Mozambique. The main factors which will determine the future global LNG outlook are:
- Changing market dynamics
- Political decisions over the environmental rules
- Global economic growth
- China future energy mix
- Europe domestic gas production
- USA shale gas industry future outlook
- Geopolitical implications
References
[1] KPMG GLOBAL ENERGY INSTITUTE, Uncharted waters: LNG demand in a transforming industry Report,http://www.kpmg.com/ID/en/IssuesAndInsights/ArticlesPublications/Documents/uncharted-waters-LNG-demand-transforming-industry.pdf
[2] New LNG markets key to growth | Energy Insights. Retrieved March 23, 2016, By James Walke, from https://www.mckinseyenergyinsights.com/insights/new-lng-markets-key-to-growth.aspx
[3] The outlook for LNG in 2016– supply growth but where is the demand?, Gas Strategies,http://www.gasstrategies.com/sites/default/files/download/outlook_for_2016_-_gas_strategies.pdf